Image Understanding (IU)
Image Understanding (IU) is the process to understand the content of images in order to automate visual tasks by computers. A visual task is some activity which relies on vision. Usually the “input” to the activity is an image or a sequence of images, and the “output” may be decisions, descriptions, actions, or reports.
The technical challenge is to make the computer understand the content of the images (image understanding) and act accordingly.
Bridging the gap between Digital Image Processing, Artificial Intelligence and real life applications is the key to meet the challenges of the 4th industrial revolution.
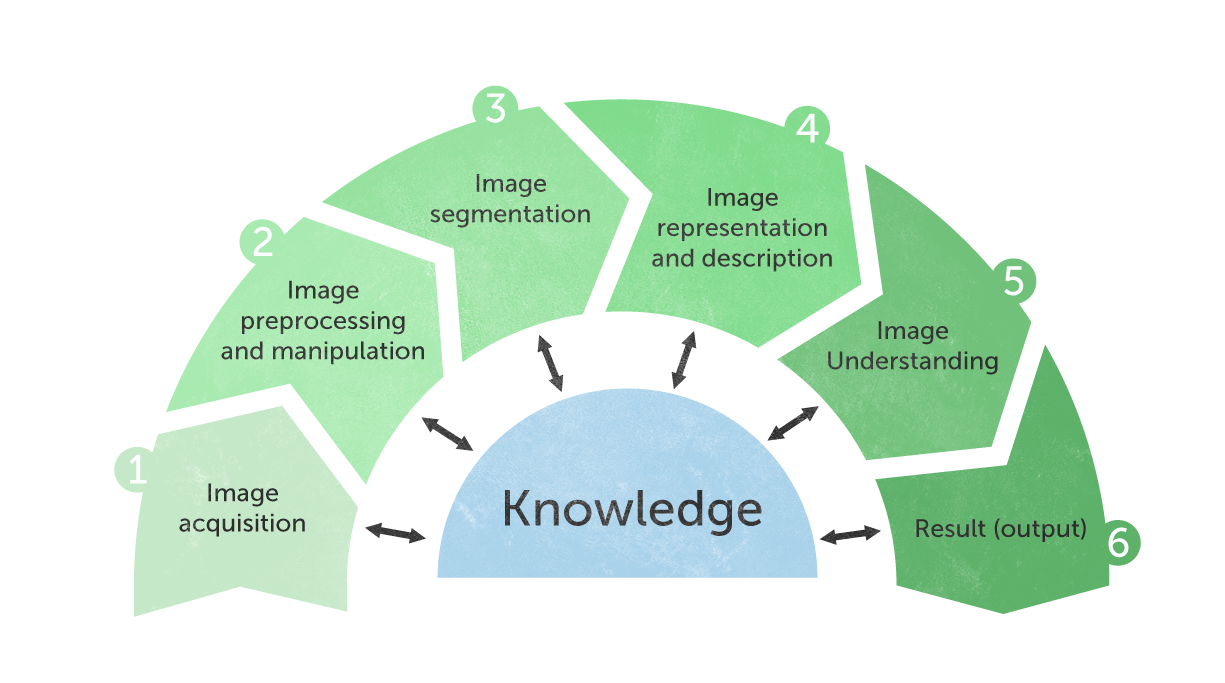
The image understanding pipeline.
In order to understand the content of of an image or a sequence of images, we have to walk through an image understanding pipeline: The pipeline consists of low, intermediate and high level processing of the image. The low level processing usually involves preprocessing such as noise- and distortion reduction and emphasizing certain important aspects of the image. In the intermediate level, the image is segmented, typically, these segments are blobs, edges, lines, corners, regions, etc. The intermediate information can then be analyzed, based on knowledge of the domain, in order to extract features, classify objects and understand the content.
Various techniques are used for understanding the content of the image . One example is “template matching” where stored geometric descriptions of objects of the domain are matched with extracted features from the images. Another example is classification using Neural Networks and Deep Learning.